The Quiet Room
The neighbors said they heard nothing. No screams. No shouts. Just the usual hum of evening life — a kettle whistling, a dog barking, the soft thud of footsteps on wooden floors. But inside the small house on Willow Street, something irreversible had happened.
Eunice Wanjiku, 29, was found lying on the living room floor, her body still, her eyes open, her breath gone. Her husband, Ibrahim, stood nearby, hands trembling, blood on his shirt. Their two children, ages six and three, were huddled in the corner, crying silently.
The knife was still on the table.
🕯️ The Illusion of Peace
To outsiders, Eunice and Ibrahim were a quiet couple. She worked at the local clinic, known for her gentle manner and warm smile. He was a mechanic, often seen tinkering with engines, his face smudged with grease. They had lived in the neighborhood for five years. No one suspected trouble.
But behind closed doors, the silence was not peace. It was suppression.
Eunice had confided in her sister months earlier. The fights were growing worse. Ibrahim had become unpredictable — sometimes loving, sometimes cruel. He would apologize, then erupt again. She had considered leaving, but the children… the children needed stability.
And she still loved him. Or maybe she loved the version of him that no longer existed.
🔥 The Final Argument
That night, the argument began over something small — a misplaced receipt, a forgotten errand. But it escalated quickly. Ibrahim accused her of disrespect. She accused him of control. Words turned sharp. Objects were thrown. The children cried.
Then came the silence.
And then the knife.
By the time the neighbors broke through the roof — the only way in after the door was locked — it was too late. Eunice was gone. Ibrahim was dazed. The children were pulled out through the opening, their faces streaked with tears and dust.
The house was quiet again.
🧠 The Psychology of Control
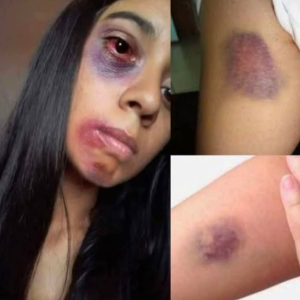
Domestic violence rarely begins with fists. It begins with words. With isolation. With subtle shifts in power. Ibrahim had slowly chipped away at Eunice’s independence — discouraging her from seeing friends, questioning her decisions, making her feel small.
She had tried to resist. But resistance came at a cost.
Psychologists call it coercive control — a pattern of behavior designed to dominate, to erase autonomy. It’s not always visible. It doesn’t always leave bruises. But it’s just as damaging.
Eunice had lived in that quiet war for years.
🧵 The Threads of Regret
At the police station, Ibrahim said he didn’t mean to do it. That he loved her. That he had just lost control.
But love is not possession. And control is not care.
The community mourned. Candles were lit. A mural of Eunice’s face appeared on the clinic wall, surrounded by flowers and messages: “You deserved better.” “We will remember.” “No more silence.”
Her sister spoke at the vigil. She held up Eunice’s diary — pages filled with hope, fear, and longing. In one entry, Eunice had written:
“I want to believe he can change. But I’m starting to forget who I am.”
🧭 The Children Left Behind
The children were placed with relatives. They asked for their mother every night. They drew pictures of her — smiling, holding their hands, singing lullabies. They didn’t understand why she wasn’t coming back.
One day, the older child asked, “Did Daddy make Mommy go away?”
No one knew how to answer.
The trauma would linger. In dreams. In behaviors. In the quiet moments when memory returns like a shadow.
But they would be loved. Protected. Given space to heal.
🌍 A Wider Echo
Eunice’s story was not unique. Across the world, women die at the hands of partners every day. Some are mourned. Some are forgotten. Some never even make the news.
But each one leaves a void — in families, in communities, in the fabric of society.
Her death sparked conversations. Town halls. Support groups. A hotline was launched. Posters went up: “If you feel unsafe, speak. If you see something, act.”
Her name became a symbol. Not just of tragedy, but of change.
💬 Final Reflection: The Cost of Silence
Eunice’s life was full of kindness. Her death was full of warning.
We often look away from discomfort. From the signs. From the quiet cries behind closed doors. But silence is not neutrality. It’s complicity.
To honor Eunice is to listen. To speak. To protect.
Because love should never hurt.
And no one should die in the quiet room.