🇺🇸 Breaking News — Major U.S. Military Moves and Orders (Latest Verified Developments)
1. U.S. Military Operation in Venezuela — Maduro Captured
In a dramatic escalation of U.S.–Venezuela tensions in early 2026, U.S. special operations forces conducted a military raid in Caracas that captured Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro and his wife, transporting them to New York to face federal charges related to drug trafficking and terrorism allegations.
This operation was the culmination of a months-long military buildup and pressure campaign directed from Washington. Venezuelan authorities and allies condemned it as a violation of sovereignty, while several Latin American governments warned of regional instability.
Key points:
-
The raid was executed by elite U.S. Army and special operations units.
-
Maduro is scheduled to appear in federal court in New York.
-
Caracas and some neighboring countries have denounced U.S. actions as illegal. (International condemnation)
This move is one of the most consequential U.S. military actions in the Western Hemisphere in decades and has raised serious diplomatic and legal questions about international norms and the use of force.
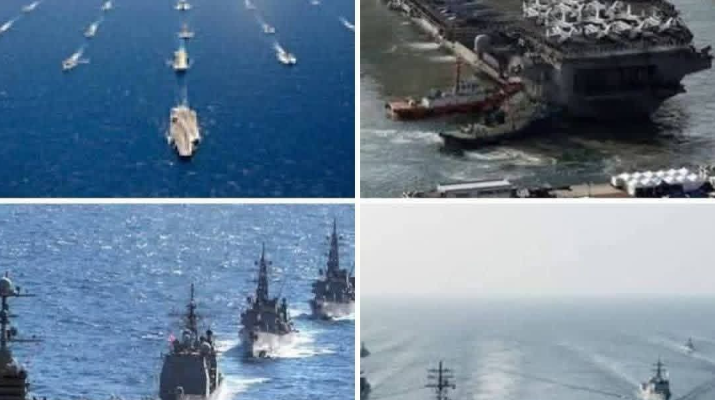
2. Venezuelan Blockade/Surrounding Claims — Military Presence at Sea
Following the Maduro operation, multiple outlets reported that several U.S. naval vessels and other assets are effectively surrounding Venezuela at sea as part of an ongoing military and economic pressure campaign.
Some media described this as a “military blockade” — a term used by Venezuelan officials and critics — though official U.S. sources frame it as part of sanctions enforcement and maritime security operations.
Reactions:
-
Venezuelan officials called the situation “irrational” and an attempt to seize control of resources.
-
Cuba and others have urged the U.N. Security Council to condemn the U.S. moves as a piracy-like act.
Legal scholars debate whether these naval actions constitute a lawful blockade under international law or an aggressive use of force.
3. U.S. Congressional Response — War Powers Pushback
In the U.S. political arena, the House of Representatives recently voted on a resolution aimed at restricting the President’s ability to send U.S. troops to Venezuela without explicit congressional authorization.
The resolution failed to pass, revealing fissures within both parties over war powers and executive authority.
Significance:
-
The vote shows concern in Congress about unchecked presidential military action.
-
Some lawmakers argue that deploying troops abroad should require explicit legislative approval.
This tension underscores an ongoing constitutional debate about the separation of powers in U.S. foreign engagements.
4. Middle East Military Buildup — USS Lincoln and More
Away from Venezuela, the U.S. is also escalating its military posture in the Middle East amid renewed tensions with Iran:
-
The USS Abraham Lincoln aircraft carrier strike group has been repositioned into the Persian Gulf region amid concerns about Iran’s nuclear program and broader regional instability.
-
Discussions continue about sending a second aircraft carrier to bolster deterrence and readiness.
This is part of what analysts call the largest U.S. military buildup in the Middle East since major strikes against Iranian nuclear facilities in mid-2025.
Why this matters:
-
It signals heightened readiness and possible confrontation if diplomacy fails.
-
Iran remains a flashpoint for potential escalation stretching from nuclear negotiations to proxy conflicts.
5. U.S. Troop Deployment Abroad — Nigeria
In a different theater, the U.S. is deploying approximately 200 troops to Nigeria to train local forces combating Islamist insurgent groups, including Boko Haram and ISWAP.
This mission is officially described as training and intelligence support, not combat engagement.
Why this matters:
-
It reflects a broader U.S. strategy of assisting partner militaries in fragile states.
-
It also ties into counterterrorism priorities dating back decades.
6. Ongoing U.S. Military Actions — Eastern Pacific Strike
Just days ago, the U.S. military conducted a strike on a vessel in the Eastern Pacific allegedly involved in drug trafficking, killing two people.
This strike continues a controversial anti-smuggling campaign that has generated significant international criticism and legal scrutiny, with families and foreign governments challenging the legality of these operations.
Context — Why All These Moves Are Happening Now
All of the above movements come amid broader strategic priorities of the U.S. administration, including:
A. Campaigns Against Transnational Threats
The U.S. has been conducting extensive military operations against drug trafficking in the Caribbean and Pacific under Operation Southern Spear and related efforts. These include naval deployments and airstrikes, aimed at cartel networks widely described domestically as “narcoterrorists,” though evidence and legal bases are contested.
These operations have involved:
-
Deployment of naval assets to the Caribbean.
-
Air strikes on vessels suspected of trafficking.
-
A formal Joint Task Force (Southern Spear) coordinating actions across the region.
B. Expanded Domestic Military Roles
Domestically, there has been an ongoing trend of using National Guard and federal troops for internal missions, including:
-
Deployments to U.S. cities for civil unrest management.
-
Creation of rapid reaction forces.
This has sparked debate about the proper role of the military in domestic affairs and raised constitutional questions.
International and Legal Reactions
Latin America
-
Venezuela and allies strongly condemn U.S. actions as illegal intervention.
-
Calls at the U.N. to denounce U.S. maritime actions as piracy or blockade.
Congressional Debate
-
Some lawmakers argue for reasserting congressional war powers after the failed resolution.
Global Dynamics
-
U.S. actions in the Middle East risk escalating tensions with Iran if diplomacy fails.
-
Training missions in Africa reflect broader U.S. counterterrorism partnerships.
What This All Could Mean Going Forward
-
In Venezuela, the situation could remain volatile. Maduro’s capture may spur protests, internal resistance, and diplomatic rifts across the region.
-
In the Middle East, the U.S. buildup is explicitly tied to deterring further escalation with Iran, which itself has warned against missteps and could react militarily or through proxies.
-
International Law and War Powers in the U.S. are under intense scrutiny, with critics arguing that recent actions bypass congressional oversight.
-
Domestic Debate over the appropriateness of military deployments at home and abroad is likely to intensify in U.S. politics.